How to Use a Structured Approach in Web Content Creation for User Conceptual Search
Updated 1.18.2022
Semantically structured web pages offering a structured approach to your content creation using Natural Language Processing for site optimization can benefit from predictive data and semantic search mapping to produce excellent results in user conceptual search.
User conceptual search gives relevant and concept information that is a related result. Your business decisions around the value of content and offering a great user experience benefit from the application of structured data when content is generated. A structured approach to content curation has evolved beyond just being critical for journalism and news sites. By drafting an organized approach to creating content using on-page markup and a focus on user conceptual search, every business website benefits.
Let’s back up for a moment.
What is conceptual search?
A concept search is also known as conceptual search. It is a form of automated information retrieval that is used in automated search to electronically source stored unstructured text. This may be a Google Dataset in digital library archives, email, scientific literature, scholarly articles, financial records, and more. It seeks information that is conceptually similar to the information used when a person conducts a search query.
Entity-based search is more efficient because a search engine can query content faster. This is what the BERT algorithm is best at.
How does concept search find related entities?
If the initial search query contains at least one concept, usage data associated with successive search queries including the ascertained concept are collected. They can then be used to determine whether a substitute word exists for a search query term that is closest to the identified concept in the initial search query.
A search system may decipher a specific context within a search query established by the adjacency of query terms to a particular query term. If a site is also going to be profit-driven, it must flow and make sense to the person on your web pages.
How do entities help structure web content?
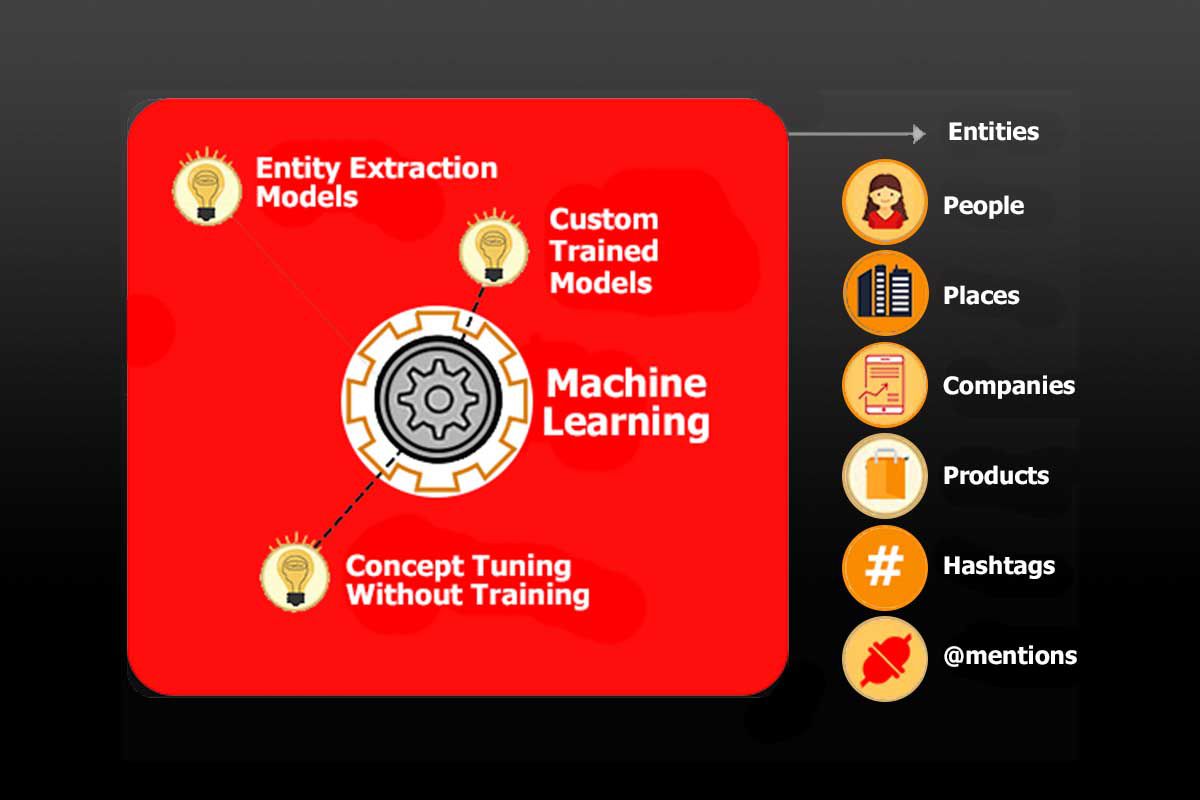
Entities help structure content better by turning language into a mathematical computation, allowing search engines to properly identify concepts and map relationships appropriately. Traditional search models simply can’t perform as well. Google is discovering how to include entity-related information in search results through augmentation queries and matching them to unique content that informs the reader and demonstrates topic expertise. This may include optimizing your web content for Google’s Knowledge Graph and Knowledge Panel inclusion.
An entity isn’t constricted by language or spelling, instead, it identifies a universally understood concept or thing. Basically, an entity is its relation to other entities. Google relies in part on nodes and edges to explain entities used in structured data and semantic search.
What is the difference between a conceptual search and semantic search?
Semantic search is a data searching process where a search query aims to not only find keywords but to determine the intent and contextual meaning of the search query.
A concept search, also called conceptual search, is the automated information retrieval process behind a search electronically stored as unstructured text for information that is conceptually the same as the information that a search query displayed. In summary, the ideas found in the information retrieved in response to a concept search query have a relationship to the entities contained in the text of the query.
A Topic-focused Approach to Structure your Content Creation
News outlets and social media channels, (be sure to include Google Posts), are inundated by raw data that they turn into content. The way they sort, categorize, publish, and store content determines if their platform meets your business needs. Your off-site content is an important aspect of your brand-building strategy and should effective to both your human audience and search engines.
If your niche seems thick with countless rivals, being able to justify your services as a better option relates to the context, clarity, and topic relevance of your content. Without a road-map and continuous flow of fresh user data reporting, it can be incredibly time-consuming to create. We talk regularly with businesses who find generating quality and unique fresh content to be expensive in terms of both manpower and financial resources that could be spent elsewhere.
Can user conceptual search provide a competitive advantage?
Yes. Providing users with quality solutions and answers that match their search query will give you a competitive advantage. Also, prepare your site to lead in visual search by meeting all image guidelines and ensure all foundational aspects of SEO are stellar.
Shifting from the former keyword-focused process to a topic-focused structured approach has led some to devalue the long, laborious process of keyword research. It shouldn’t be set aside, but rather matured into today’s approach. Additionally, after creating buyer personas that identify your audience, whether you are in a B2B business market or B2C, you can move forward faster with confidence and success in visible search results by using a structured approach to topic entities.
Artificial Intelligence Uses Everyday Natural Language
The expanded capability of humans to be able to talk to machines using everyday natural language to gain relevant search results is increasing. Search engines and Google Artificial Intelligence can comprehend the intent behind a search query, not merely the exact keywords used for search. Google’s release of RankBrain, a machine principally functional for long-tail queries, relies on concepts of semantic search. Tasked daily with 15% of all search queries being completely new to Google, semantic search helps Google cognize web articles readily. When your business article ranks for keywords that don’t actually exist anywhere in your article or in anchor text, it is benefiting from LSI keywords or the ability to match search intent semantically.
A recent in-depth look at 1 million Google search results by backlinko.com revealed a change in Meta title tag correlation. This is the association between a specific keyword in the web page’s title tag and changes to ranking in SERPs for that keyword. Today the role of the title tag has significantly shrunk. Whereas it used to be imperative to place an exact matching keyword or a similar one, now search works differently and without such a need to be explicit with title keyword being targeted, thanks to Google gaining a better understanding of the context of the article.
This contributes to why long-form web content is growing in favor. It is better capable of fully answering user questions on a given topic and is thus attributed by search engines as having higher relevance. Quality content that is answer-rich helps you win visibility in immediate Google SERPs.
A site’s content keywords lists found in your Google Search Console provide the most significant keywords and their variants Google notes when crawling your site. When studied in tandem the Search Queries report and your site’s listing in actual search results for your targeted keywords, it yields critical insights into how Google is interpreting your web content.
Use a Structured Approach to your Content for Natural Language Processing
Many internet users are unaware that they are communicating to a rudimentary AI if they use online support. Many of these chat support bots are actually automated responders. While it can feel like they miss your intent, some are truly able to extract knowledge from your business website and respond with correct answers to customer queries.
Savvy chat bots must be proficient at understanding natural language processing, which previously was a huge challenge. Adding the essential types of schdema markup will increase search engines understanding of pages. Customers customarily talk in a manner that is vastly different from how computers talk. Creating machine learning that translates both is rapidly advancing natural language processing (NLP) and uses a structured approach to matching search query intent.
Search has morphed from “words” to “concepts, or entities.” Grasping what words actually mean as well as the association between the words in digital content, is what makes up semantic search. Search is much more visual. Consider the popular product carousels.
The competence to decipher meaning and intent behind words is “artificial intelligence. Google Now may be your first recognizable form of AI. Just as we “speak” to our smartphones, a transition is taking place moving to where we talk to our computers as much as type.
RankBrain Focuses on Long-tail Queries
Gary Illyes of Google indicated at Pubcon that RankBrain doesn’t change how other algorithms work.
It’s key focus is on long-tail queries and negative search queries and bases its determinations by evaluating the historical performance data for related structured queries. From a machine learning perspective, this is sorted out by assessing how alike a specific query is to historical queries in high-dimensional vector space analysis. Google attributes historical performance of such related queries to render rankings results for the new long tail query in real time.
RankBrain strives to use signals to adjust rankings based on the query and is currently the best algorithm at processing new queries.
Solving Search Limitations of GSE’s
As more mobile buyers favor making purchases online, Google search is pressed to evolve from a general text corpus into a varied assembly of documents, and targeted retrieval approaches must be created to meet the demand for more precise information needs. This means that Product schema markup is important for mobile queries.
Today, this is better achieved by using structured queries to apprehend the semantics meant behind a user search query and strives to glean domain-specific ranking functions to represent the hidden semantics of object classes that a site’s web pages comprise. GSEs are constrained to simple keyword queries while in comparison, structured queries frequently involve data field semantics (e.g. numerical constraints) and demonstrate field inter-dependencies.
“General search engines (GSEs) are sufficient for fulfilling the information needs of most queries. However, they are often inadequate for retrieving web pages that concisely describe real-world objects as these queries require analysis of both unstructured text and structured data contained in aclweb.org
10 Examples of How Commonly AI’s Structured Approach is Used
1. Online purchase predictions
2. Services suggesting movie and music options
3. Privacy and property security surveillance
5. Intelligent digital personal assistants*
6. Scientific discovery
7. AI prototyping
8. Google data-based news generation
9. Self-driving smart cars
10. Credit card fraud protection
“Your smartphone, your car, your bank, and your house all use artificial intelligence on a daily basis; sometimes it’s obvious what it is doing, like when you ask Siri to get you directions to the nearest gas station. Sometimes it’s less obvious, like when you make an abnormal purchase on your credit card and don’t get a fraud alert from your bank. AI is everywhere, and it’s making a huge difference in our lives every day.”
Search Engines Match Buyer Query Intent Differently from Informational Queries
When aligning your business for both paid search marketing and organic search visibility, action queries are by far the weightiest in user conceptual search.
A search query is generated by a user wanting to “do” something, like “buy a travel ticket to Washington DC.” Informational queries, on the other hand, are for users wanting to “know” something, i.e. “how can I increase conversion on my website?”
The better a page clearly matches query intent by using all of a page’s semantic signals, over time, the better it will rank for that search query. As the Google BERT algorithm advances, exact phrase matching in web copy isn’t as vital as it formerly was. In fact, it can really hurt you if it tips into “keyword stuffing”. Digital content peppered with loads of keywords in the copy no longer generates top search results. It is better to spend more time optimizing your Google Business Listing.
Your Semantic Index comprises the part of Google’s algorithm that determines what your website is about and how much it truly relates to its given topic compared to other sites. In technical SEO terms, such semantic “signals” encompass items like the URL, Title Tags, META keywords, image tags, META description, internal UX structure, author’s topic expertise, outbound links, Google reviews, and mentions/references/citations.)
With the growing value of incorporating dataset search, like Oracle and PostgreSQL, and new emerging multi-type Cloud databases, new graph capabilities to relational databases are emerging. Dr. Nicolas Figay says this means that “a standardized graph querying language is not concerning only 1,5% of the databases, but quite more.” According to the Nov 22, 2019, The emerging landscape for distributed knowledge, ontology, semantic web, knowledge base, graph-based technologies and standards article, site’s with good structure show up better in knowledge graphs.
This is because KG’s are a special kind of database that draws upon trusted, cataloged knowledge in a machine-readable form. This means that a website’s categories and should be considered with some caution so that search engines can best interpret them. Additional graph query language support is likely why ISO language requests are more frequent and need more diverse solution providers.
How to Structure Content to Best Align with Customer Intent
Identify the customer’s intent and know what keywords or queries are really driving at” the People Also Ask and Related Questions in SERPs. If you are asking, when did a focus on semantics begin? Or how accurate is it? They are great questions.
Semantics in ontology mapping gained an early 96.2% accuracy reading.
In response to the growing number of non-English language web documents, back in 2006 Google provided a localized and region-based search engine. “The ontology mapping accuracy is 96.2%; the accuracy of the ontology tagging is estimated to be between 60% and 70%”, according to the Dec 1, 2006, Ontology based text indexing and querying for the semantic web article ****. Since then much has been accomplished to close the gap between the HTML based internet and the RDF-based vision of the semantic web. By linking words semantically in texts and entities to concepts of ontologies, topic ideas can be better identified and matched.
Understanding and implementing ontology mapping can give small business a chance to compete in competitive SEO niches.
Plan a Structured Approach to Reach Buyers with Intent to Purchase
It takes a holistic SEO strategy to make awesome content. Marketing research will map the topic opportunities with keywords data to get the search volume and gain the desired SEO traffic. Learn how to layer your keywords together to make meaningful content. We continually refresh our keyword list and then carefully analyze the SERPs for each search phrase. Then see how Google viewed the intent of each query and next choose the more transactional keywords — i.e., the keywords people would use when looking for the particular products and services the client provided.
If Google can see that users are engaging your content, it should make sense for your site. Run a technical SEO audit to remove any hindrances. The best sites’ are about the user experience and content. You don’t even need the keyword in the content to rank for it, but you must have content that fits with those searches. It is necessary to have sufficient content to rank for content – create a marketing plan for where you need supporting content versus head content.
US Google and Luth Research examined the consumer path to purchase journey*** and how semantics and user results create the core of your digital business. The data was analyzed between April and Aug. 2016 and observed cross-device clickstream data on four individuals’ responses to opt-in leads.
Two key buyer search trends emerge around holiday shopping preferences:
(1) Searches evolve as people zero-in on what they really want
(2) People turn to search to “gut check” what brand, product, or retailer best meets their needs.
Three Basic Types of search queries used on the Internet:
(1) Informational
(2) Navigational
(3) Transactional
David Amberland** suggests using content that can be found online and repurposing it in a way that helps your site to rise above competitors. Integrate clever interlinking, the speed of processing, and the sheer volume of the number of reports you generate to become the go-to hub for trusted information in your niche that prospective buyers are seeking.
Effective Content Curation Tactics and Semantic HTML
Design content with a structure semantically arranged by filter intent. Past web retrieval systems were more limited in connecting relevant information, being largely based on keyword matching. Today, web content should be prepared for Voice Search. It was inadequate for the vast amount of data available and provided limited capabilities to apprehend the concepts of the users’ wants and the correlation between keyword phrases. These limitations lead to the transition toward the user conceptual search which has matured to including concepts and meanings. Marketers creating semantic HTML posted content are sectioning their ideas into structured categories as a better approach to content curation. They rely on new Artificial Intelligence technologies that are reshaping search trends.
A 2014 study on the Semantic-Based Information Retrieval System for semantic web searches offered a value-added algorithm capable of retrieving the information in a more competent manner. This more structured architecture utilizes input from a list of traditional keywords provided by user history and converts the search query, voiced or typed, into a semantic query. This ability is made possible with the help of domain concepts from preexisting domain ontologies, independent thesaurus, and advanced capabilities to decipher semantic relationships between them during runtime. Applicable information for the semantic query is used to determine rankings according to relevancy.
Aspiring beyond word-based Information Retrieval (IR) Systems to content-aware and context-aware scenarios are prevailing. Today, semantics plays a large role in a content strategy using structured documents and mechanisms to extract semantic information from the documents. With the development of new Internet-enabled wearable gadgets and the burgeoning use of smartphones by mobile buyers, the need for additional data by the Information Retrieval System designers is pressing. The necessity to interact with users and context is a cornerstone in providing solutions to ongoing issues.
According to semanticscholar.org, “The ranking technology is based on the estimate of the probability that keywords and concepts within an annotated page are linked one with another in a way that is the same to the one in the user’s mind at the time of submitting the query. The probability is measured using a graph-based description of ontology, user query and the annotated page”.
To optimize your content for viewers and business goals, it should be comprised of strategic choices that drive business revenue. We live in a semantic metadata-focused world where taxonomy management and how posts, documents, and pages are classified. Craft and execute a metadata-rich environment to have semantic-intelligent web content served top in SERPs when users need it. Having a web presence at this level of sophistication is useful in the following areas: improves earned search, data records management, brand identification, privacy issues, intelligent migration, secure partner collaboration, content and text analytics, and any web application or process that requires the use of metadata. Hire a digital marketer who knows how to keep your structured data current.
Web designers who start by working in partnership with SEO’s who possess data structured content marketing skills gain more relevant traffic to their sites.
QUESTION: Does schema markup help concept search?
ANSWER: YES. We can help you understand your business’s current position in SERPs, semantic mapping, and the order of your existing online history to offer users actionable prompts. We also help businesses determine what long-tail keywords are missing in the delivery type of your search terms, chart which page might rank for better organic conversions, and draft a plan on how to figure out how to write to it. This route is much better than throwing up content and then learning how it works.
Then we apply various tools to your situation to find the highest probability of sales and how to market your curated content. For AdWords display, unofficially, will see a decline in organic ranking when dropping PPC. PPC advertising tends to drive “incrementally more clicks” if your site is first ranking in the top three positions organically for the same search queries. For example, a pain management clinic in Plymouth MN can be a specific niche and a business located there needs to make sure that they are ranking for the right service sale versus information. The intent of long-tail is more important than head keyword terms. We help our clients discover what they can leverage to get current wins driving for the search intent you want to match.
We recommend using a structured content methodology that includes e-Commerce microdata to ensure that the right content on your site is served up to the right viewer at the right time. By creating a good structure, you can use the content you’ve written more effectively. 42dm.net hosted a Business Growth On Hyperspeed webinar that I highly recommend for more information on user conceptual search.
NOTE: All web pages will also benefit from PageSpeed optimization using Web Core Vital metrics. Great content still gets missed when people won’t wait for slow-loading pages.
User Conceptual Search and Graph Data Modeling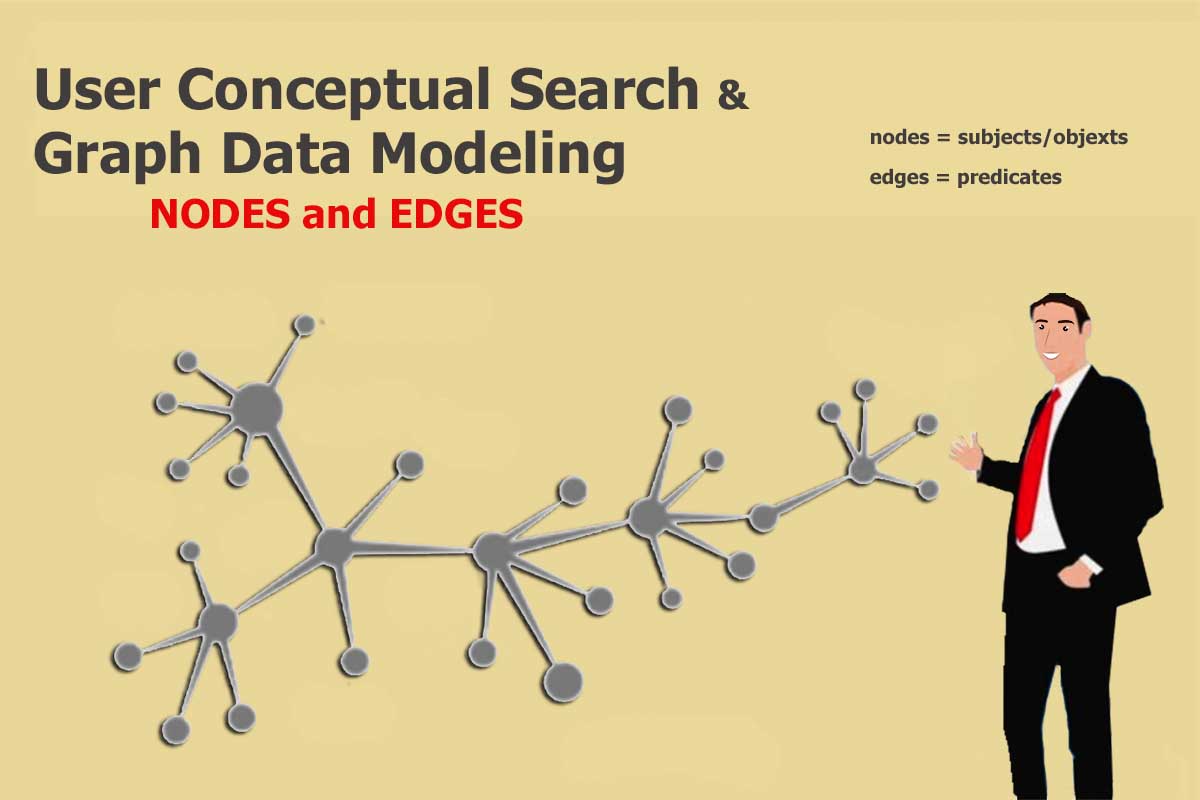
On March 28, 2019, Ivelina Nikolova, PhD discussed with Ontotext the foundations of graph for creating structured web content . He states: “Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a graph data model that formally describes the semantics, or meaning, of information. It represents metadata, i.e., data about data RDF data model consists of triples that represent links (or edges) in an RDF graph.” *****
These entities can help you match your prospective buyers search intent to align your key content to what matters most to them. Since how users search and find a relevant answer is done much by machine learning today, structured web content is more important than ever.
The scaling of traditional search techniques to grasp data of magnitude is challenging enough for most small to mid-sized businesses. New technical challenges surface that are involved with using the additional information present in hypertext to produce superior search results.
Here is a FREE help: Download our SEO analysis guide and dive in. We can take your business forward with an in-depth site audit.
Structuring your onsite data is so important, it should be included in all Beginner SEO Guides, in our opinion.
 Owner of Hill Web Creations, Jeannie Hill has years of experience and positive results for clients by training on a structured approach to web content that improves results for user conceptual search. I team with clients to help you understand your online data and make better choices. We strive to significantly improve search result precision through its use of conceptual retrieval.
Owner of Hill Web Creations, Jeannie Hill has years of experience and positive results for clients by training on a structured approach to web content that improves results for user conceptual search. I team with clients to help you understand your online data and make better choices. We strive to significantly improve search result precision through its use of conceptual retrieval.
I live and work in Minneapolis, Minnesota, providing digital marketing services to local businesses and national clients. If you employ these search strategies, you will know that your SEO is effective.
Action Steps for Your Business to Embrace Graph Data Modeling
Give your business a boost by collecting data, interlinking, and search entities extraction as a part of text mining. Shape your business knowledge graphs by integrating a structured approach by using unstructured data in addition to facts from open source knowledge graphs. If you are serious about your business’s future, preform multiple types of website audits to find a structured approach. Read up first on common search marketing FAQs to better understand the terminolgy used.
Consider your current search results. If you don’t find them to be precisely what we are looking for in each case, enlist our services to move past “general” Google search and get the Digital Results Wanted from Your Marketing
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intelligent_personal_assistan
** https://www.davidamerland.com/seo-tips/1035-structured-data-or-a-structured-approach-to-content-making-choices-for-your-business.html
*** https://s3.amazonaws.com/luth-wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/17165141/Luth-Whitepaper_Unlock-Your-Imagination-for-Digital-Data.pdf
**** https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222566181_Ontology_based_text_indexing_and_querying_for_the_semantic_web
***** https://graphdb.ontotext.com/free/devhub/rdfs.html