How Author Schema and Bio Pages Build Author Authority
Google wants content publishers to remove doubt about who the author of an article is.
Every search engine wants to be the trusted platform for searchers seeking correct information. This tasks them with how to discover trusted authors. Before most content marketing managers will add author transparency, they want to know why it is important. This article will cover the best ways to demonstrate author authority.
Develope a long-term Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) strategy over quick wins. For example, not every reader can distinguish an article providing medical advice from an eager medical school graduate with no experience over a doctor writing with years of proven skills and case studies.
In our free speech society, a lot of opinions are written and published. Too often, statements are downright untrue versus providing factual and accurate information. While an author’s intent may be good, when opinion is confused with truth, it may be harmful; this is especially true in the area of healthcare question answering. Today, it is common courtesy to let the reader know who wrote the page. Likewise, if you were searching for information about how to build your website’s authority, you’d consult a semantic SEO professional versus a web designer who is more knowledgeable about how it looks.
Table of Contents
Author Authority is a concept that describes the authority an individual author has accrued up the web of data for a certain topic. Author Authority is the level of trusted recognition an author has obtained for their recognition as an expert. Website owners generate more value for your organization’s content when you attribute authorship to on-topic authoritative writers. Authors may influence a domain’s authority based on the credibility of the publication’s author.
To follow this, December 2023, Google announced Profile Page Schema for Organizations and People. Many people are not authoring content on a domain but have a significant role in the business entitly. Same as for authors, this will help search bots understand organizations and people with a profile page much better.
Everything that market research identifies for a “phrase” contains the process of named “entity-query” association. If associated with author sources, it may factor in behind the scenes as to how they are ranked with distributed relevance and authority. Authors may establish a Personal Brand Panel; while they are not a quick win, they are powerful influencers.
Authorization of knowledge panels on search engine results pages (SERPs) is growing; it becomes a profile on the SERP. You need to provide Google with a fundamental understanding of your key authors. Additionally, general sentiment from reviews that mention your business name along with a person’s name can affect your entity node association.
It can be very important that the author is trustworthy.
“Author” is taken from the word “authority”. It is the author who gives authority to whatever he/she produces. The Latin words for “author” and “authority” come from the same root. They’re derived from a word that means to invent, trustworthy writer, responsible person, or to promote. When a topic authority writes, they are adding value on the web in a sea of low-ranked content pieces. In Latin, it literally means “one who causes to grow”, a “source of authoritative information or opinion.” [1]
If you are worried about how you’ll stack up as an author with the increase of content by chatbot authors, being established as a trusted source will make a difference.
We value adding author bylines as a reader benefit. They can help searchers understand context and authorship when they want to determine the content’s trustworthiness. However, quality content can rank without a byline, especially on a site with strong E-E-A-T signals. Domains that use them commonly exhibit additional characteristics of useful content that satisfy Google. Bylines alone will not rank your website. However, when they do accompany helpful content, a trusted site, and other factors, it can be a successful strategy.
Is author authority a ranking factor?
No. Having a topic expert write articles published on your domain doesn’t magically make you rank better. There are several reasons why:
- Any individual could self-declare themselves to be an expert. That means nothing or little without backing the statement up.
- Ideally, Google quality raters can identify a writer with topic expertise as it has become self-apparent across the web and checks out in SameAs Person Profile schema or otherwise.
- “Ranking” isn’t the first thing to focus on. Rather, care about your users, online conversions, and how to improve sales.
What would be a good thing is having an expert write content that people like and appreciate because the expertise they have is self-apparent. If people appreciate your content, you can naturally gain actual singles that are used to reward people-first satisfying content. [11]
No one should declare that author authority is a page ranking factor. However, multiple Google patents have been filed to help them identify authors for individual web pages. Google’s patent uses “digital signatures” to rank content based on reputation scores. US20040003248 patent tells us that “Conventionally, digital signatures are created and verified using public keys, and are being used to identify authors/co-signers of electronic data”.
Author is a Schema property that can be added to Schema types within the CreativeWork or Review classification, such as Article, NewsArticle, MedicalScholarlyArticle, and TechArticle. This property is valuable as markup for the author’s byline that informs readers and search engines about who wrote a piece of content. For YMYL sites, it becomes an essential schema markup type.
Google uses its own data to determine what content piece by which author to serve up. Schema markup is incredibly helpful. The more definitive and transparent you are about your website’s authors the better. Authorship schema is in your control in your programmable search engine. Your strategy to increase click-through rates can include these measures to build an author’s Google Profile and provide readers assurance of value.
Concepts like expertise and authority are derived from something other than someone taking your word for it. Concepts to decipher expertise and authoritativeness can be gleaned by search engines by taking the word of their users as a whole.
Schema.org specifies how to use the “authorAvatarUrl” property for “author.” We find it to be helpful among other similar formats.
Search engines seek trusted author sources when recommending content.
Every search engine knows that when its users are searching for information on its platform, they prefer authoritative sources. If something they click on doesn’t resonate with them as truthful or relevant, they might opt to use another browser. Whether directly or indirectly, we see Google saying more about Expertise, Authority, and Trust. It matters whether or not you declare to search engines who wrote a post.
The fact that author reputation and credibility are now specified within Google’s quality rater guidelines is noteworthy. These documented instructions ask its raters to discover mentions of a site or author in external “news articles, Wikipedia articles, blog posts, magazine articles, forum discussions, and ratings from independent organizations”. We should do the same.
Successful search marketing includes grasping where Google’s endeavors to go as well as current tactics. Author Authority is increasingly important because of the influx of fake news. When a true topic expert writes, Author Authority decreases the level of fake news that major audiences have to sort.
We recommend adding “By author…” just under the title of blog posts and other informational content. Just like a book has the author on its cover, this specifies the author of each page upfront.
Why this matters to your SEO and content marketing strategy:
- People are asking; “Q. How can I determine if an author is credible?” or “Q. Does the author have expertise on the topic about which he/she is writing?”
- Google’s Quality Raters are instructed to identify verifying information about authors when manually evaluating websites.
- If you don’t declare it, authorship may be assumed.
- This may build trust; it’s a core aspect of semantic search. It helps you manage your knowledge graph on the linked open web.
Different authors have unique writing styles, article tones, and varying levels of expertise in different topics. Google’s comments suggest in its patent on author vectors, it may have the ability to identify the authors of unlabeled content. The content a site publishes, its topic hubs, along with each post’s author’s topic authority contributes to how E-A-T is assessed.
This really matters when you are seeking to build your web of connections. It creates a data thread between the author and all various pieces of content they’ve written. Potentially, it may feed the new article carousel for more well-known authors in knowledge panels. It is common for healthcare-related content to have it peer-reviewed. A peer-reviewed publication is commonly referred to as a scholarly publication. The peer-review process means that an author’s scholarly work, research, case study, or ideas have the benefit of the scrutiny of others who are experts in the same field (peers). It is valued as a way to ensure accuracy and academic scientific quality.
Is a Good Writer the Same as a Topic Author Expert?
No. A topic expert is someone who knows the topic inside and out. They know what is factual about the topic, what is opinion-based, what daily questions are asked, ect. This is very different from a writer who starts from a keyword-based approach.
Rather, a good writer knows more about how to make a good first impression, create a strong ending, get to the main topic right away, organize their articles and stories, etc. It is better for a good writer to engage a topic expert than to write on topics that they are not recognized as an expert on.
For example, if you are looking to learn how to provide premium plumbing services, do you want to learn from a writer who can only copy ideas from someone else? Or follow an article template? Or learn from articles written by a certified plumber who has been hands-on plumbing work for ten or more years? Likewise, search engines are looking to surface articles by real niche experts.
Similar to the answer to this question: “Question: Do I need to be an expert on a topic to write a good book? Answer: No, you don’t have to be an expert to write a book. But you do if you expect anyone to read it.”
How does an author become an authority?
To write with authority, present your thoughts easily, clearly, and with confidence. Set an authoritative tone by writing in an active rather than passive voice. This is accomplished by putting the subject before the verb. Authors who consistently publish on trustworthy websites have their credibility and authority documented on the SERP. In our experience, long-form topic-specific articles work best. This comprehensive topic coverage also builds the authority of the publisher’s platforms that features expert authors. Comprehensive topic coverage and relevant, trusted content sends both direct and indirect signals to search engines.
An author’s primary bio page is quickly becoming their new, modern business card. It’s your digital assessment of your brand SERP. Google is assessing how credible your authorship is, what your expertise is, and how broadly you are trusted and known. This is your chance to represent yourself the way you want. If this page is a fair representation of you, it will inform search engines of why your writings are important to your audience.
Google may understand the author of an article better if their name links to a profile page.
Creating an author bio and using author schema helps build your author brand SERP.
The author’s Profile Page or Bio Page gives the details as to why the author is a trusted expert and authority on a specific topic. Writing your author bio well merits taking sufficient time to make its content valuable to the reader. Experience and a recognized, digital person brand SERP are important. This may assist in establishing your relationship with your audience. This helps you manage your exact match brand SERP. A strong author profile page is your chance to be proactive versus reactive to your brand SERP.
Businesses that declare their content authors may avoid many reputation management problems. This becomes more important if you publish medical, scholarly, or academic articles.
A Person Brand SERP is the result Google returns for a search on a person’s exact name match. It is important because it can establish the main attributes of your author entity. If search engines understand the attributes of the author entity, they are able to classify that entity. In turn, the author’s writings on a specific vertical gain stronger confidence.
Additionally, including content reviewers also establishes good transparency and trust. Third-party references help search engines identify topical relevance from higher-ranked author authorities. Once your answers are proven as better, Google may choose what you write about and update its answer-rich SERPs. On client sites we manage, each of our author pages makes it clear that topic experts are actually writing the content. It’s not hired out to a novice.
If the author has a website, their About page is very important. It becomes the main resource about the author.
What elements should an author profile page include?
Author profiles should include details that show their depth of experience and expertise in a certain niche.
- How they gained their work experience in the field, such as education, internships, and consultations.
- Organizations they are associated with: nonprofit expertise volunteered, where they were a keynote speaker, group leader, article reviewer, etc.
- Industry affiliations such as if a vendor requests a product review, where they hold memberships or serve on a board.
- Awards and recognitions they have won in their field of expertise.
- Author accomplishments listing reputation-building publications.
- Links to pages backing up their authority on domains such as Wikipedia, Crunchbase, and interviews on well-known websites.
- Published articles on other authoritative, niche sites.
- Personal hobbies, interests, and/or research that have developed their expertise.
Within a site’s WordPress dashboard go to the menu named ‘Users’. Add or select an existing user’s name to display the input fields. In the setting window related to the author’s information, click on the “Display name publicly as” and add the author’s name that you want to be displayed.
A WordPress manager can add authors, contributors, and editors to your blog by inviting them through the dashboard “Users” tab. Each role has different responsibilities. For example, an author can edit and delete their own posts and upload images, but they cannot edit other areas within the dashboard. This protects the business owner and the author from unintended mistakes that may even take a site down. However, in our experience, it is best for the author to write and send the written document to a skilled SEO who knows the many nuanced tasks of optimization before hitting the “Publish” button.
WordPress posts by an award-winning author should leverage this approach to draw attention to the content piece. We do this even if it is a single post that fits under “short stories”.
What is an Author Knowledge Panel?
It is easy to identify Google News author knowledge panels. They are large information boxes displayed at the top of the SERP when a user searches for an authoring entity. Search engines are data banks. They store and use systems designed to understand facts about entities in the web of data and how they relate to each other. This impacts search rankings. Google automatically updates the author knowledge panel if data information about the author changes.
In our experience, strong team alignment across marketing, content, and SEO teams helps authors gain this type of awareness in Google Search.
We learn from Google that “Knowledge panels are updated automatically as information changes on the web, but Google also considers changes in two main ways: directly from the entities depicted in the knowledge panel, and from general user feedback.”[2] Meaning that you can influence your knowledge panel.
This makes it important for authoritative authors to claim and influence their author knowledge panel. Jason Barnard covers this well.
“Getting a knowledge panel on Google is not limited to famous authors… Google has no concept of notability, it is simply trying to understand. It is up to you to provide the facts about the author and build Google’s confidence in its understanding. Once it has the facts about the author and is confident in those facts, you will get a knowledge panel.” – The 3-Step Process to Getting a Google Knowledge Panel for an Author by Kalicube
When no article author is given, the authority of the content piece is based on the reputation of the publisher or domain the article is published on. An organization can be considered as the author. However, for YMYL sites, expertise, authority, and trust is established when a topic expert author is provided.
An article’s author URL entity has existed for a long time. What is new occurred last year when Google recommended adding an author’s URL to article schema to assist in article author disambiguation. Author schema helps to identify the correct author when several writers have the same or similar names.
John Mueller of Google talks about how author pages can be helpful for some content topics and explain why you should try to demonstrate author authority.
The above April 23, 2021, English Google SEO Office Hour reflects where Google is at on Author Authority and why it may matter.
“When it comes to things like author pages, or information about the author… our systems try to recognize who that is, what that entity is, we do that based on a number of different factors. It does include links to profile pages or visible information that we can find on these pages themselves. At least link to a central place where you say everything comes together for this author, which could be something like a social network profile page, for example… so we can group this by entity. We try to use structured data to explicitly apply this… We do try to understand who the entity is behind an author page… We call that reconciliation when it comes to structured data – kinda recognizing which of these entities belong together.” – John Mueller
A quick look back will provide context.
– Google Patent US9378293B2 was applied for June 3, 2004, and the application was granted on June 28, 2016. It is titled “Method and apparatus to author and manage pages of a website” [3]. It involves the system and methods to use an author markup language (AML) to define output pages. It is based on an author schema that defines the correct vocabulary for AML.
– We saw the Google Agent Rank US20070033168A1 Patent in 2005.[4] It included author reputation scores that would potentially boost page rankings which could be influenced by the identity of authors, reviewers, editors, or commentators contributing to a page’s content.
– In 2011, the Google+ platform gave authors a significant opportunity to verify their identity, manage their personas, and establish author authority. In turn, this gave Google improved search quality but matching trusted content authors to related search queries. This helped birth online authorship as demonstrated in its Authorship markup and web search article. [5] Google+ authors were permitted to link content to their personal profiles.
– Also in 2011, Google begin adding showing author pictures in combination with a person’s profile for articles that contained the authorship markup rel="author". This triggered many marketing strategies for Author Authority. Google later deprecated this authorship markup. Yet the concept of Author Authority lingered. It surfaced as relevant again when it was directly referenced after Google updated its Search Quality Rater Guidelines (SQRG) just prior to the August 1, 2018, Google update.
– Just two years reports surfaced that Google officially killed authorship. Gary Illyes from Google said it is finally safe to remove authorship markup from your pages. Later, Gary said don’t remove authorship from your pages, that Google may still use it. We know they used it for in-depth articles still, but not anymore. He said they have other ways to know who wrote which articles and no longer depend on authorship to determine it. So it is safe to remove authorship from your pages.
How does Google Recognize an Author as a Topic Expert?
Google can recognize which author is the primary writer; it recognizes the same writing patterns and identical syntactic construction. Like a fingerprint; an author is identified.
Goole Author Knowledge Panels are ideal; however, for most authors, begin with a declared entity home. Google’s John Mueller recommends to “link to a common or kind of like a central place where you say like everything comes together for this author which could be something like a social network profile page (or entity home) for example. Use that across the different author pages that you have when you’re writing so that when our systems look at an article and they see an author page associated with that, they can recognize this is the same author as the person who wrote something else and we can kind of group this by entity and we do that based on maybe this common social networking profile that is there.”
Relating to the topic of adding author schema, he said “we call that reconciliation when it comes to structured data, kind of recognizing which of these entities belong together.”
When seeking to gain a Google News Author Knowledge Panel or an Author Knowledge Panel, John recommends using a consistent author link to a central place where everything comes together helps when you are writing so Google’s systems can recognize the author and group by entity. While Google no longer uses rel author annotation using structured data, article authorship schema plays a powerful role today.
WARNING: It is not right for a site owner, or another individual, to be randomly changing the declared page author(s). It is recognized as “very strange” and looks manipulative. Why would you keep changing authors randomly on pieces of content??? Just add the author that wrote the content, be clear; be honest. If you are simply quoting someone in your article, that doesn’t make them the author. Nor does reviewing or editing an article.
NOTE: Healthcare article types have been reported as favored if they indicated when an article piece is “peer-reviewed”. This form of expertise or correctness is important and effective; the peer reviewer does not become the author. More concisely, their role is clear and demonstrates the accuracy of an article’s content.
– Reputation of an Author of Online Content US Patent 8150842B2 was granted to Google on April 3, 2012.
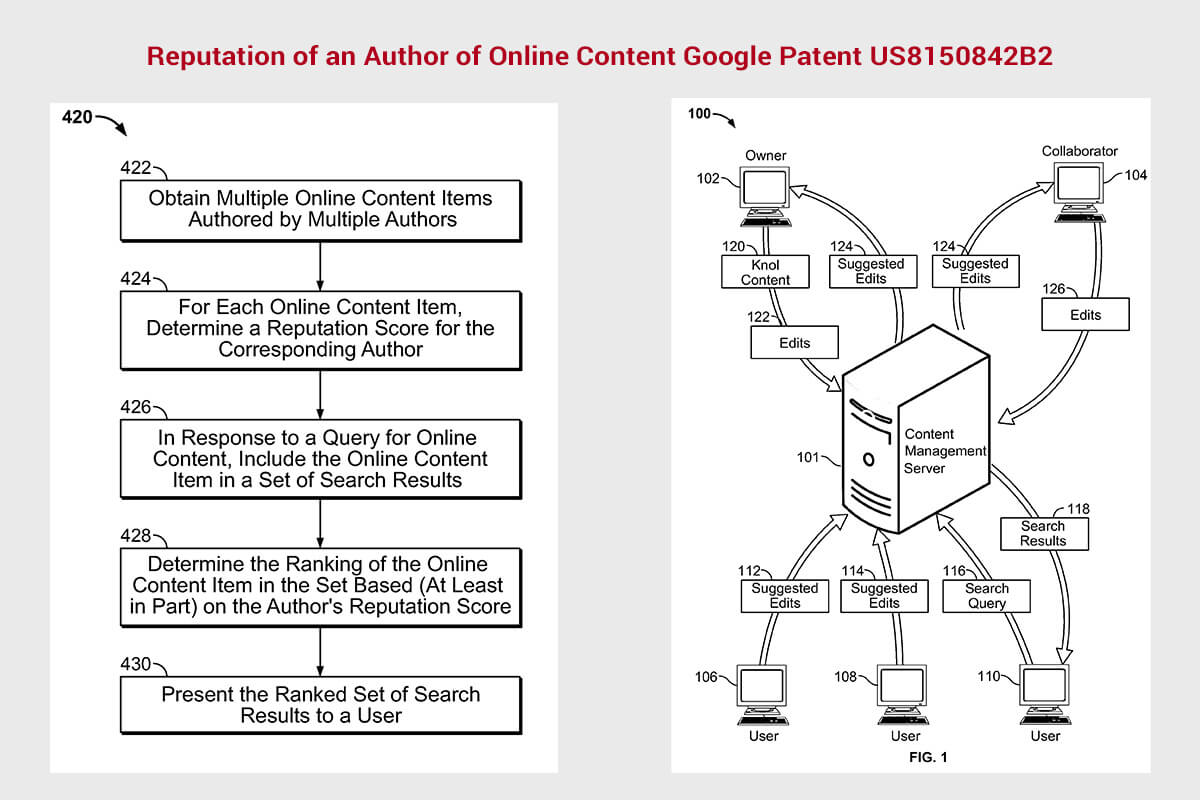
The Reputation of an Author of Online Content Google Patent sheds light on Google’s selective process to understand the authorship, and authors’ reputation. Cohesion between the main content creator and the domains helpful content scoring, produces a higher confidence score (E-A-T). But, if a website has many content creators, and an author only has a few content pieces attributed to them, or content that does not trigger many query responses, or does not meet information gap or value needs, may not be served to searcher as often.
Google’s System and Method for Confirming Document Authorship leverages author ID verification. In addition, an author’s online content reputation assess the author’s reputation, and how shares, quotes, followers, and other methods, authenticate them for a topic expertise.
– Generating Author Vectors US Patent 62165966 [7] was granted to Google on March 24, 2020.
“Methods, systems, and apparatus, including computer programs encoded on computer storage media, for generating author vectors. One of the methods includes obtaining a set of sequences of words, the set of sequences of words comprising a plurality of first sequences of words and, for each first sequence of words, a respective second sequence of words that follows the first sequence of words, wherein each first sequence of words and each second sequence of words has been classified as being authored by a first author; and training a neural network system on the first sequences and the second sequences to determine an author vector for the first author, wherein the author vector characterizes the first author.
Text classification systems can classify pieces of electronic text, e.g., electronic documents. For example, text classification systems can classify a piece of text as relating to one or more of a set of predetermined topics. Some text classification systems receive as input features of the piece of text and use the features to generate the classification for the piece of text.”
– On August 6, 2021, Google’s Developer documents add the following line: “Add a new recommended author.url property to the Article structured data documentation. The URL property helps Google disambiguate the correct author of the article.” [6]
– In 2021, Google Quality Rater’s Guidelines updated to include a section that focused upon an article’s creator reputation. This informs us that web pages’ content creator still seems to be something that Google seeks to understand. Whether or not, or to what extent author reputation matters to Google is a topic that the SEO industry vyes back and forth with different views as it plays catch-up to possible algorithm changes.
“We expect some form of website information for many or most websites. We expect clear information about who (e.g., what individual, company, business, foundation, etc.) created the MC (main content) unless there is a good reason for anonymity. A long-standing Internet alias or username can also serve the same function as identifying the MC creator.” – Section 6.6 of Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines
How to Implement Author Schema
- Append the Person type with the url
Authorproperty. - Nest the author URL within your Article schema, a webpage that uniquely identifies the author of an article.
- Alternatively,, use schema’s
sameAsproperty to further disambiguate the author, for example linking to their Wikipedia page. - Validate author code using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool before publishing.
- Link to a web page that uniquely identifies the author of each article.
When multiple authors contributed to an article, schema experts can use a JSON array to list all of the authors and links to their bio pages. We list the main author first and additional authors by their level of contribution.
Example:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"author": [
{
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Doctor's name and title",
"url":"https://www.site/author-1/"
},
{
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Tamara Scott",
"url":"https://www.site/author-2"
}
]
</script>On July 1, 2022, Google added information in its article structured data documentation for author markup best practices. It encourages adding all the authors of a web page are included in markup. Instructions are clear to notmerge multiple authors in the same author field.
Here is the example multiple author markup code provided:
"author":
[
{
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Willow Lane",
"jobTitle": "Journalist",
"url":"https://www.example.com/staff/willow-lane"
},
{
"@type":"Person",
"name": "Echidna Jones",
"jobTitle": "Editor in Chief",
"url":"https://www.example.com/staff/echidna-jones"
}
],
"publisher":
{
"name": "The Daily Bug",
"url": "https://www.example.com"
},
// + Other fields related to the article...
}
Are Google Answers Attributed to Google Author Rank?
Yes. It can associate authors who want to give answers to certain questions to related topics. Google Answers has broaded to include multiple SERP featured snippet formats as well as including communications on social channels. Google is refered to as an “Answer Engine” for good reason; this question answering content may also populate People also ask boxes.
How Google may determine which authors have topic expertise:
- Google can create an authorship profile and recognize question answering communications.
- Google engages feedback by authors that may influence the expertise level of the author.
- Google can associate data left in reviews and online comments to the author’s success.
- Google can aggregate and catalog data for serving up quality answers from trusted authors.
Implement a Schema.org type Person to inform readers who authored this page, its topic, where to find the author’s about or bio page, and social media profiles. Currently, the best solution is pointing author URL markup to the person’s bio page that details their credibility and links to their social media profiles. This helps by creating multiple signals to search engines and readers that help to decipher the correct author and why they merit listing to.
Establishing “Author Rank” or the authority of the author
For authors, your personal brand SERP is assisted by linking to the same social media profiles everywhere you publish. These identifying entities should also be added with schema markup. This consistency helps establish the difference between you and another writer with the same or similar name.
Avoid confusion. Author structured data code is different from Publisher structured data markup. The publisher is the organization, magazine, or government entity on whose domain the content piece is published; authorship is who is the content writer.
In 2018 Mark Traphagen authored this perspective on Perficient:
“Bottom line: I don’t think we have sufficient evidence to say whether Google is using any kind of author authority in search. However, we do have evidence of an increasing (and renewed) interest by Google in identifying authors. If your content is meant to project the authority and reliability of your brand, then it makes sense for users to see that it’s written by credible subject matter experts. (Bonus: you’ll be all set if Google ever does crank up ‘Author Rank‘!)” – Does Author Authority Matter for Your Content and SEO?
Why should author pages link to social media profiles?
Including the author’s social media profiles will help readers follow them when readers resonate with an article. It also confirms an author’s niche involvement and authoritativeness. Author Rank may be improved when an author is clearly a leader or has “influencer” status.
Social media profiles may boost Author Rank by:
- Giving more people a chance to read the article.
- Your followers get to see the real you in a more conversational setting.
- Increases engagement.
- Shows that you are active and present for critical in-the-moment conversations.
- Creates an node entity association with other authoritative people in your field.
Creating high-quality authority signals for writers
These semantic schema types help to establish the authority of the content on your website by displaying author boxes. Add a reference link along with the writer’s social media profile links to connect the author with high-quality authority signals. One example is how many followers the author has. Depending on how you elect to add your schema code, what is important is clarifying you Author Schema Entity.
Implementing Author Schema Markup makes it easy for search engines to validate topic experience and expertise. By adding the worksFor property, you reinforce the person’s relationship to the organization the author currently works for. The sameAs property for the Author entity is where we add social media links. this also works for the website URL and may include additional profile URLs.
This assists in distinguishing the author from similar names as well as assesses their credentials. Both users and quality raters want to determine the writer’s credibility, credentials, or affiliations. In the case of blogs that permit guest authors, if the worksFor property is already included within your organization info, you don’t need it.
How do readers know if an author is a topic expert?
If you find the author has a Author Knowledge Panel that is powerful confirmation. If you find a person has author several articles within niche publications, that is great confirmation. It separates them from “Ghost Writers”, largely written AI articles, or a hired writer without niche expertise. Look for a descriptive author bio that validates their niche expertise.
Readers are getting smarter – especially if they are at the beginning of research for a major purchase. They are looking for proof that an article’s author is a true topic expert and what they say can be trusted.
Academic journals are written for experts in an academic field and the articles are contributed by expert scholars versus a “content writer”. An author of a scholarly (or academic) article typically includes his/her credentials or affiliations. Commonly additional topic references are provided in footnotes, endnotes, etc..
Google is building an entity understanding of the author based on the links from the authors articles and other factors.
“Credible sources are written by authors respected in their fields of study. Responsible, credible authors will cite their sources so that you can check the accuracy of and support for what they’ve written.” – Whitworth University [8]
“Not everyone is an expert on every subject. That’s why you’re in college, after all — to get a degree in a field of study that will help you get a job. As you gain experience in your chosen career, you grow in expertise. You may even publish articles and books of your own! But until you’re an expert yourself, you’ll need to rely on the publications of those who have gone before you.” – American Public University System [9]
Hill Web Marketing Services for Building Content & Authorship
We do a lot of content management and understand how to display and build author credibility.
Google has author icons in its article carousels. While we tailor our service packages by niche and budget, one way this works is using the following suggested format.
- The subject matter expert writes an article (considered as a draft).
- A good writer with SEO or publication writing skills refines or re-writes the article (with minimal changes to keep the expert writer’s “DNA” expertise as the main content writer).
- A independent (average person) reviewer reads and weighs in on readability, flow, and what the user experience is like (Understandability: Are next steps clear?, Are they assured that a topic expert wrote the main content? Do media assets explain/enhance the content?).
- A medical reviewer if for the healthcare niche; or corresponding reviewer if for
ReviewNewsArticle, aNewsArticle,TechArticleand/orCriticReview. This individual provides a professional critic’s assessment of a service, product, performance, accuracy, and/or topic relevance. - A search marketer with audience, ontology, knowledge graph inclusion, schema markup, Metadata, media formats, distribution channel expertise, as well as reviewing for topic accuracy, grammar, factual, and style.
Likewise, a niche article that takes advantage of FinancialService Schema, AccountingService Schema, BankOrCreditUnion Schema, InsuranceAgency Schema, etc., benefits by a topic expert writer, reviewer, and/or approver at the “influencer” level. For businesses with low budgets, or just getting serious about content marketing, only 1 and 5 listed above may be needed. (We prefer at least 1, 3, and 5.) Success will depend in part on the topic competition level, demand, and how strong the Brand SERP is.
“We know that great content comes from great authors, and we’re looking closely at ways this markup could help us highlight authors and rank search results,” states Google. [10]
“I think it’s fair to say that most users actually do often care about bylines, so in that sense, it is an SEO factor, just like all other SEO factors that relate to user experience & trust. Make the kind of webpage you would want to read yourself. Fake authors are not it.” – Lily Ray 😏 (@lilyraynyc) [12]
“So if people know that your brand is synonymous with whatever it is that you’re trying to do, then you probably can succeed just on the E-E-A-T of your brand. But otherwise, we really all should be trying to have authors that are known as the experts in our field.”
…but the point is here (adding author schema) you want to give search engines and users as much information as you can to say yes this is who is responsible for this content and here’s why we think he or she is most qualified to write about it.” – Dr. Marie Haynes [13]
Why you should care: Google entity search is surfacing more information about your business entity, the authors, and your page to searchers, making it clear to them that they can trust the site, authors, and content on the page is increasingly important.
Google SERPs now surface other “Perspectives” around topics that currently rank well in top stories. Searchers want to learn what others have to say about your site and authors.
Conclusion: How Google Attributes Author Authority
The credibility of an author is very important in determining the quality of the content piece. Schema Markup will highlight your authors, empowering you to inform search engines about your content experts. To scale and leverage structured data to win rich features and grow converting traffic, Hill Web Marketing can help you!
Call 651-206-2410 and request our Schema Markup Audit and Opportunity Discovery Services
References
[1] https://www.etymonline.com/word/authority
[2] https://support.google.com/knowledgepanel/answer/9163198
[3] https://patents.google.com/patent/US9378293
[4] https://patents.google.com/patent/US20070033168
[5] https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2011/06/authorship-markup-and-web-search
[6] https://developers.google.com/search/updates#august-2021
[7] https://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=10,599,770.PN.&OS=PN/10,599,770&RS=PN/10,599,770
[8] https://libguides.whitworth.edu/c.php?g=702696&p=5086997
[9] https://apus.libanswers.com/faq/131345
[10] https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2011/06/authorship-markup-and-web-search
[11] Search Liaison https://x.com/searchliaison/status/1755283334631231514
[12] https://x.com/lilyraynyc/status/1744847088985219357
[13] https://www.mariehaynes.com/author-eat-webinar/

