How to Analyze Drops in Google Search Traffic
One or multiple reasons can cause a site’s traffic decline. That makes analyzing why a site experiences a Google traffic drop is harder.
Someone with experience and understanding of healthy backlink profiles, proper .htaccess file, robots.txt file structure, the use of redirects, knows what is helpful content, and more is required. Significant traffic drops can equal serious business revenue losses. It is too easy for a novice – much less a skilled person – to unknowingly makes a change that impacts traffic flows. Ultimately, losing relevant, action-taking site visitors is directly tied to business revenue streams.
Table of Contents
- How to Analyze Search Traffic Patterns Using your Google Search Console
- How to Analyze Drops in Search Traffic
- Evaluate if poor UX means losing site visitors
- Research if a search traffic drop is related to Google algorithms
- Determine if you’ve lost featured snippets
- Check your site’s robot.txt
- Audit for Schema markup drift
- Assess possible duplicate content issues
- See if the site has indexing and/or crawl errors
- Search log files for recent website changes
- Check for a Google penalty
- Check if your marketing plan is structured effectively
- How to Monitor Web Traffic from Google Search Console by Daniel Waisberg
- Google Discover Traffic Updates Based on User Demand and Habits
- How to Monitor People’s Topic Interest Levels Using Google Trends
- Can Technical SEO Issues Hurt Web Traffic?
- What is the best Plan of Action to Avoid Google traffic Drops?
- Benchmark your Website against Niche Leaders to Determine Content Helpfulness and Reliability
- Updates to Google’s Debugging Traffic Drops Documentation
- SUMMARY: Stay on Top of Factors that may Cause Traffic Declines
The recent Google core updates in March have significantly impacted businesses, causing a drastic drop in website traffic. This is an urgent situation that requires immediate attention.
We’ve seen the biggest change in Google Search last month and this month. The search giant has removed up to 40% of “unhelpful” content from its index, and many who feel impacted are wondering what to do. We find that investing in audits and SEO schema provides insights and a roadmap to recovery.
Additionally, Google has taken more manual actions. Understanding and knowing what to fix due to these overlapping updates can be difficult. The average business owner doesn’t know where to begin or lacks the time or expertise. You may need to reassess your business plan and budget to recover.
How to Analyze Search Traffic Patterns Using Google Search Console
The following tips are on a high level and cover the best place to start.
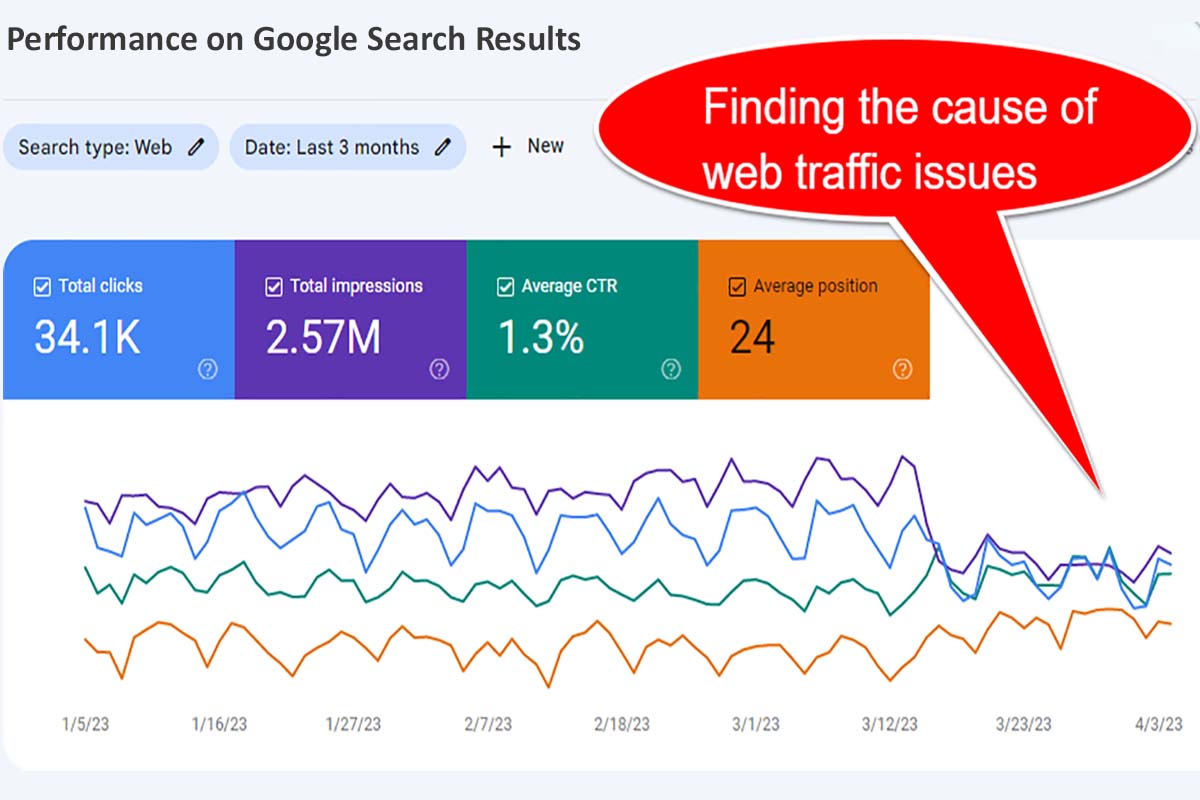
Use the Search Console tools for web traffic assessments by:
- Navigate to the Performance Reports.
- Compare date ranges.
- Assess where the drop is: videos, images, across the web, or in Google News (top stories).
- Look for consistent changes in traffic levels. Select tabs that display charts showing total clicks, total impressions, average CTR (click through rate), and average position for each property.
We like to keep in mind that sitewide drops typically occur faster whereas page-level drops show up more slowly. Diagnosing what happened to your search traffic is best done with a continual eye on it over time. For example, if it is due to a Google reporting bug, normal traffic levels will return. Set up an alert to be notified of such incidents.
Another way to keep in the know is by following an expert like Barry Schwartz’s or Marie Haynes’s search reports.
Google Search is continuously and rapidly evolving towards a Semantic, Multimodal, and AI-powered Search Engine. This influences what content it deems is most useful to surface within its search engine result pages (SERPs). How well your digital marketing and SEO teams keep up impacts your web traffic levels.
Google tells us to “See how your search traffic changes over time, where it’s coming from, and what search queries are most likely to show your site.” One of my favorite reports is to compare data between two values in any one grouping dimension. We can sort by difference to identify queries with significant change from the previous week.
Depending on your history and niche opportunities, look at your FAQ rich results report, product snippets, and aggregate data by page rather than by property. Glean insights on questions your audience wants answered; it can gain you SERP visibility when people query further by asking follow up questions.
How to Analyze Drops in Search Traffic
Below are a few ways we typically monitor site traffic and identify why a drop may occur.
- Evaluate if poor UX means losing site visitors.
- Research if a search traffic drop is related to Google algorithms.
- Determine if you’ve lost featured snippets.
- Check your site’s robot.txt.
- Audit for schema markup drift.
- Assess possible duplicate content issues.
- See if the site has indexing and/or crawl errors.
- Search log files for recent website changes.
- Google penalty (can be either manual or algorithmic).
- Check if your marketing plan is structured effectively.
Let’s dive into more detailed ways to accomplish the above tasks.
1. Evaluate if poor UX means losing site visitors
In today’s hyper-competitive web of data, providing a great customer experience is essential to sustain organic Google search traffic. Customers expect personalized and painless UX experiences. Web pages that fail to meet these user expectations risk losing buyers to their more customer-centric competitors.
2. Research if a search traffic drop is related to Google algorithms
In recent years multiple Google updates occurred. Some were pre-announced and we could prepare for it, others were a surprise. Widespread changes in traffic across dozens of sites we watch seemed to be significantly impacted.
Often, the recovery advice we give is similar to our general recovery consultation. That is to check the value of your content. Google is increasingly better at determining searchers’ intent and serving up pages that are relevant to that intent and have good Experience Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) scores.
If you are negatively affected by a Google algorithm update there is no way to ascertain for sure that is the cause of your traffic losses. No alert message displays in your Google Search Console. However, we have had email messages from the GSC of a significant spike in traffic to a specific page. It helps to check if the same traffic swing is happening within your Bing or Yahoo data reports.
If the traffic decline is only found in Google traffic and this coincides with an announced Google algorithm update, it’s more likely that Google’s updates are the reason behind your drop.
3. Determine if you’ve lost featured snippets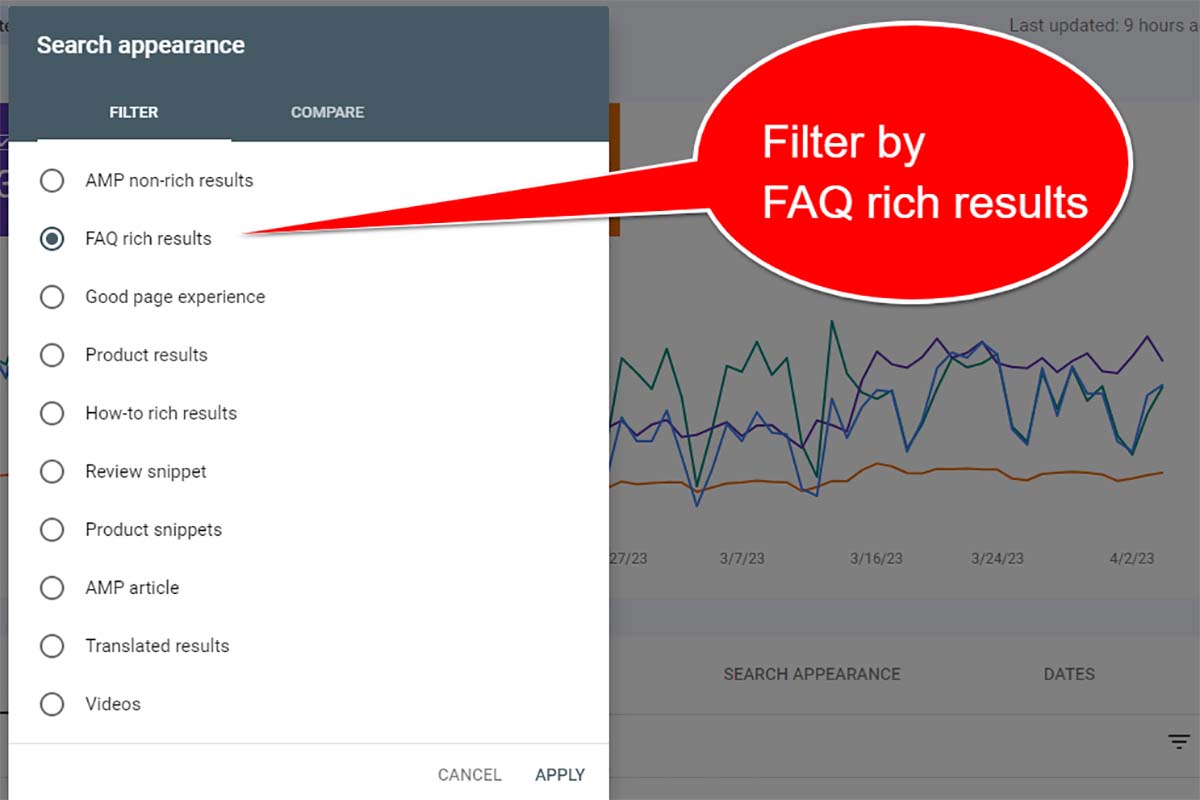
Featured snippets can drive a lot of traffic to your site. It’s important to become and maintain being your audience’s go-to source for answers. You may need to level up your SEO if your former FAQs and How-Tos that were winning featured snippets are now lost to a competitor.
Today, winning more web traffic is a lot about providing high-value content. A lot of query answers are found in People Also Ask boxes. If you formerly showed up and now do not – that may mean a loss of clicks coming from the SERP.
Recently Lily Rae responded to Glenn Gabe with the following comment on Twitter: “Wow, quality raters’ work has *shifted* to reviewing Bard AI answers – instead of Google’s search results, presumably? Not good.” [1]
A key place to check is your Google Search Console FAQ data report under Performance > Search appearance > FAQ.
You can actually use Bard or another Generative AI tool to create a list of individual pages’ main topic frequently asked questions and provide answers. A SERP evaluation and alignment with Google’s rich result guidelines can bring traffic levels back up. Natural Language Generation (NLG) refers to using artificial intelligence (AI) to generate written or spoken copy for content suggestions.
4. Check your site’s robot.txt
If the domain’s traffic suddenly drops to zero (and your site is live), your robots.txt file could be the culprit. A sitewide noindex tag may have been left in place after a web redesign or mistakenly added. On a page level, “A page that’s disallowed in robots.txt can still be indexed if linked to from other sites. While Google won’t crawl or index the content blocked by a robots.txt “, Google’s document states. [2]
John Mueller just responded on Twitter with “You are safe from any noindex attacks if you protect the site with robots.txt though.” [3]
5. Audit for Schema markup drift
Schema.org was created with the core intent of helping Internet users find the content they are conducting a search query for. It only works if you’re maintaining schema markup to avoid drift on a regular basis. If you have too many errors and warnings on a particular page, Google may decide to drop it from its index until the issues are resolved.
Broken or schema code with errors can mean you’re missing the web traffic you were enjoying from rich results. We’ve definitely seen traffic losses regained by correcting the client site’s markup. As well, to much markup (often repeated by multiple plugins doing the same task), may bog page load speed. This matters because visitors who have clicked to access a page may leave rather than wait.
6. Assess possible duplicate content issues
Too much duplication can easily occur. A content brief before publication will help your writers stay tightly themed to the page’s unique purpose. A content audit across all publications will reveal where someone forgot a post from years ago that covered much the same topics. If you don’t have a new and needed angle on a topic, it may be better to tweak the former post.
Excellent duplication tools include:
- Siteliner
- Smallseotools
- Plagiarism Detector
- Duplichecker
- CopyScape
Don’t leave it up to on on-site search or search engines to try to decide which page is most relevant to the query. This is partly why we love content briefs.
7. See if the site has indexing and/or crawl errors
This is another way you should use the Google Search Console. Open up you’re Index Coverage Report and look for any URLs that have an Error. URLs found in the coverage report that have an error status won’t be included in Google’s index.
Common errors discovered in this report include:
- Server errors (which so often go undetected otherwise)
- Redirect errors (or inappropriate HTML status codes)
- URLs blocked by robots.txt
- URLs that are marked with a no-index tag
- Soft 404 errors (that may still be worth correcting)
- URLs that return an unauthorised request
- URLs that Google Bot cannot located (404s)
- Other Crawling errors
8. Search log files for recent website changes
If you experience a drop in traffic following significant changes being made to your site, go back and evaluate those changes. If needed, use log files to determine what was done by who and check if the timing aligns.
Common website problems caused by changes that result in traffic loss:
- Someone added too many or incompatible plugins.
- WordPress theme updated or was changed and caused havoc.
- Internal links disappear during a site redesign.
- URLs changed or dropped without proper redirects put in place.
- Significant design or page content changes. We check the homepage first.
WordPress lets you easily review page revisions. Also, archive.org is an ideal tool like to see which on-page elements, text, or link changes occurred that may have triggered the traffic drop.
The entire site plummeted “When a CMO decides they need to change the copy on their homepage because of an article they read”, Sean Johnson shared on Twitter on April 4, 2023. He added the comment: “Unfortunately this happens a lot to niche sites when a CMO does their own keyword and topic research trying to milk more revenue out of their site without doing things that work but cost money.” [4]
We experienced this recently with an owner who wants to make unplanned content strategy changes and then we “fix” or “optimize” them afterward. They had added so many huge/overweight images and videos to one page, that no one could even get the builder to load the page’s contents to make repairs. Looker Studio’s data visualization can be very efficient in conveying drops. to individuals who are less technical.
As well, a web designer or developer was unfamiliar with our article schema markup code, and so they removed it. This may have also contributed to a loss of web traffic.
9. Google penalty (can be either manual or algorithmic)
Google penalties can cause a traffic drop. Google posts its essential site core practices “that can have the most impact on your web content’s ranking and appearance on Google Search”. [5] While anyone can get a picture or text to show on a page, the guidelines need to be followed if you want consistent traffic. To earn and maintain more traffic than your competitors takes skill.
Fewer sites we evaluate are being penalized by Google these days. But you may lose significant web traffic without ever getting a penalty warning. This is why we highly recommend monthly or quarterly technical SEO audits.
“Manual actions happen when your website does not follow Google’s guidelines. Some pages or the entire site may be less visible from Google Search results through manual action.” – Daniel Waisberg, Search Advocate at Google.
10. Check if your marketing plan is structured effectively
While assessing individual areas of traffic drop causes, also evaluate if you simply need an overarching different marketing plan. It may help you to better align with your followers and active audience. Especially if your site needs to incorporate ways that it is additionally serving a new or different purpose.
By understanding a business’s core KPIs and main goals we typically start with one of seven different types of marketing plans. From campaign planning, content creation, outreach, brand reputation building, and audience targeting, to digital transformation, the right SEO strategies and marketing plans will influence your traffic ebbs and flows.
So, we know these tasks may seem daunting. However, it is simpler if you have the right tools and know how to use them.
How to Monitor Web Traffic from Google Search Console by Daniel Waisberg
Recently Daniel Waisberg talked about this and his answers are insightful. There can either be internal reasons or external reasons. Internal causes may be unintended mistakes someone makes while creating or updating a page. External causes may be as simple as a shift in user choices. It could be that you no longer have a competitive lead. Google will favor the most accurate, helpful, and concise answer from a trusted source.
“In addition, if you sell a specific brand online, there might be a new competing product cannibalizing your search queries.” – Waisberg
He suggested two basic ways to assess low web traffic using Google’s tools: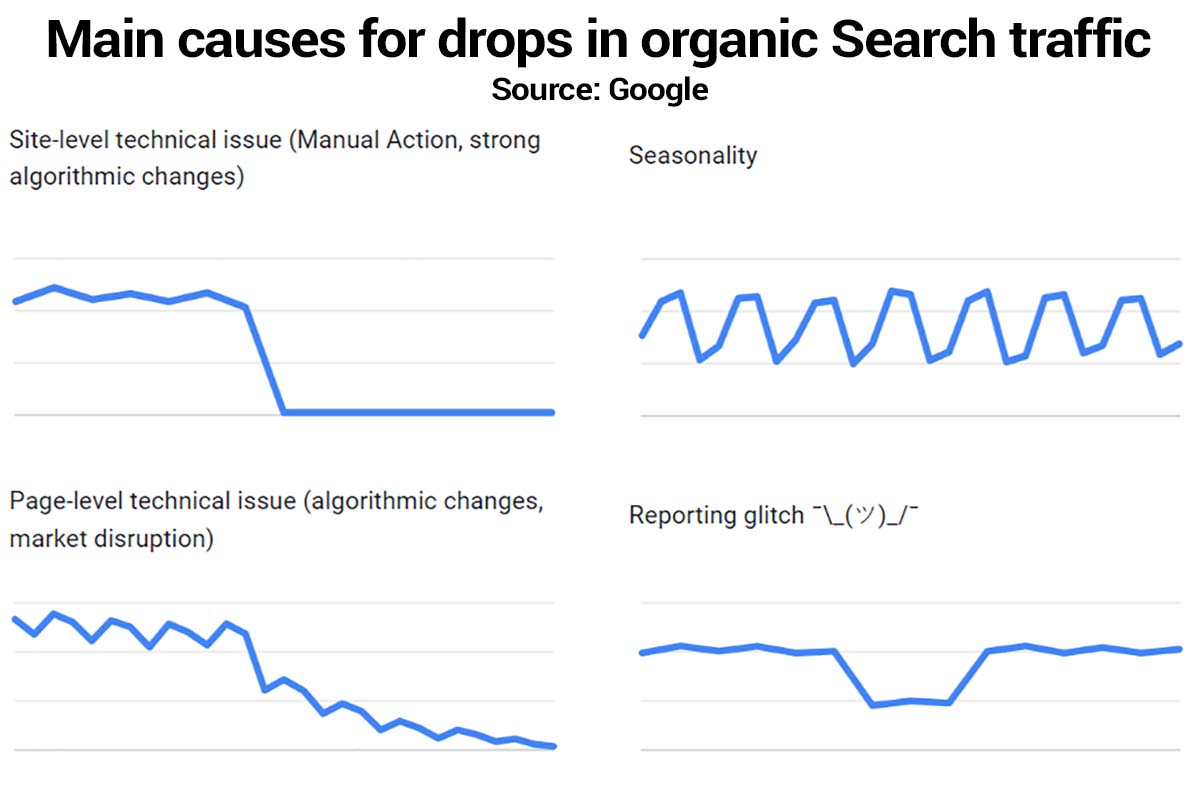
Google updated its Debugging drops in Google Search traffic documentation on 9.26.2023 and included a handy new graphic. Its helpful for learning what is potentially affecting your Google Search traffic. [7]
- Use Google Search Console
- Use Google Trends
How Waisberg bucketed typical reasons for a drop in traffic:
- Site-level technical issues (some potential reasons: the site is down or manual actions).
- Page-level technical issues (some potential reasons: no index tag on the page, search interest disruption, or Google algorithm update).
- Seasonality (like, lawn care during summer and snow plowing during winter).
- Reporting glitches (Google tries to communicate when this is an issue by providing chart annotations).
“Another factor that could drive a slow decline in traffic is a Search interest disruption. Sometimes, changes in user behavior will change the demand for certain queries, either due to a new trend or a major change in the country you’re looking at. This means your traffic may drop simply because of external influences.” – Daniel Waisberg
Additionally we evaluate losses in the Google Search Console by viewing clicks or impressions. Average position numbers can vary a lot so we rely on them less. Useful data is also found in Google Analytics reports. SERPS can adjust to reflect changing user search intent due to seasonality. Analytics data can also confirm these seasonal traffic ebbs and flows.
Google Discover Traffic Updates Based on User Demand and Habits
Google Discover organic traffic is a feature that updates according to the demand and habits of users. Generally, helpful content that is indexed and aligns with Google’s content guidelines can be included in Discover. However, that fact remains, Google Discover traffic is challenging to predict and will ebb and flow.
It is helpful to understand how Google Discover works since it reflects how the selection process is tied to what users want to see.
How to Monitor People’s Topic Interest Levels Using Google Trends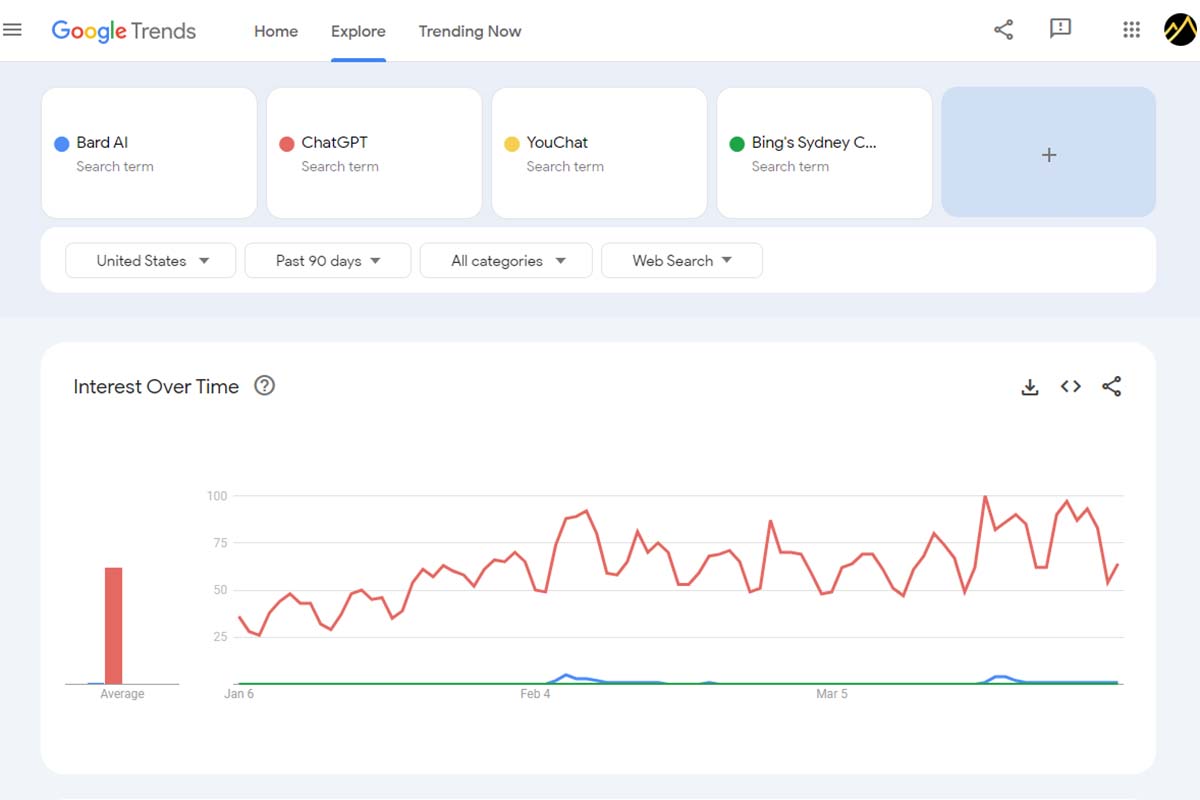
This tool populates real-time, unfiltered search data from actual users. It provides many ways to view Internet user trends, so I recommend trying them all and finding what offers the most valuable insights for your marketing research.
How to use filters in Google Trends to research topic trends:
- Worldwide or segmented by Country
- Time range
- Web search or Image search, Google Shopping, News search, or YouTube search
- All categories or segmented audiences (Examples: Health, Internet & Telecom, People & Society, Reference, Science, Shopping, etc.
For all topics, this tool lets you also check what’s trending right now on Google Search. After using Google Trends to evaluate traffic drops for clients, I often use the “Export, embed, and cite Trends data” to share with other team members.
Scroll down further to gain a “Breakout” under “Related Queries”. These insights may help you win visibility in “Related Searches” on the SERP.
Can Technical SEO Issues Hurt Web Traffic?
Technical SEO may negatively impact your traffic flow if:
- Missing, duplicate, or confusing page titles: Your site has overarching technical issues and your competitors have them basically resolved. Like errors in your robots.txt file as discussed above, missing or poor title tags, broken image links, etc. Broken internal links restrict link equity flowing throughout your site, which impacts rankings negatively. Conversely, strong and effective interlinking helps.
- Broken or lost external links: Not all backlinks are created equal. If you notice a lost link of high relevancy and trust, especially a local one, it can cause declined traffic. This may be a combination of its absence means that people don’t find it on that external domain to click on. (For example, if you let go of a Chamber or BBB placement. These two profile links are key for brand entity recognition) Or there are losses due to the link juice it formerly provided. In some cases, if you lose a significant number of valuable links pointing to your domain, it could cause you to lose ranking positions.
- Poor Core Web Vitals: Google’s user page experience scores have been discussed in detail, but overall we lacked finding them to carry much impact. While another cause is more likely, recently, this may have been an issue for one client. Their WordPress theme updated and over 2 seconds to every page’s load speed. The timing aligned with a drop in the GSC. We are still investigating other causes.
-
Poor site migration or web redesign: Avoid Google traffic dropping due to a site migration. A common cause of a sudden drop in website traffic is due to recent site migration. While time alone helps, there are several things to check before pulling the trigger. Are redirects in place? Have you made significant AI content or UX changes? A web design update can work either way.
We’ve been called in after a site redesign that went wrong and found that the focus had largely been on visual components. They are important, indeed, but site visitors care more about getting answers and information than being dazzled by flashy page elements. If you recently redesigned, migrated, or relaunched your site or updated from HTTP to HTTPS and see a noticeable drop in Google traffic, you most likely didn’t have a website design firm that could manage the complex transition plan.
- Lacking a good mobile experience vs desktop: If your typical site visitor uses mobile devices when conducting a search, you need to have very mobile-optimized content. If certain web pages struggled to get indexed, ranked, or found useful, take time to inspect these pages. They may have page elements that fail on mobile, be weak in the content, or lack action steps. Updating them can make a difference. Is the content vastly different that what a person using a desktop sees?
- Orphaned pages: These are web pages that lack internal links pointing to them. Each published page should have a distinct purpose worth linking to. When you value them enough to reference them with internal linking, you are telling Google that they are important enough to be in the index.
What is the best Plan of Action to Avoid Google traffic Drops?
Most significant and sustained drops in Google Search traffic can be avoided.
The best advice is – don’t wait until your site is suffering from a lack of web traffic. Be very proactive and customer-centric by knowing what your active audience needs and ensuring that you show up at each stage of the consumer journey. After your audit has determined the cause, putting the following in place will assist in protecting you from future drops.
Your action plan to avoid repeat traffic drops can include:
- Build a Web Traffic Monitoring Dashboard
- Invest in tools that your team needs.
- Make sure time is allotted to do audits.
- Assign one individual (or team) to this task so that it doesn’t mean you don’t have to be “reactive” to losses.
- Be active in forums or on Twitter where your peers may be sharing the same issues. Listening is an excellent skill!
- Embrace agility. Make quick changes that show your consumers and Google that you care and continually offer more value. As new SERP features emerge for queries with transactional intent, how buyers make purchases is continually updating.
- Weisberg encourages us to “go from the monitoring to exploring mindset.” By closer alignment with Google’s Quality Rater guidelines, you can focus on more traffic versus recovering from losses.
- Periodically export and store data to future traffic comparisons. You can download more than 16 months of information.
- Audit and optimize your Google Business Profile.
You can create a Google Search Console dashboard in just a couple of steps using Google Data Studio. Or hire a professional who knows how to setup the data insights that you want to monitor.
Another thing to consider is what changed on Google’s side. For example, if you recieved a lot of Google Search traffic from FAQ rich results and HowTo pages, the tech giant is trying to declutter its SERPs where these have been overused.
Benchmark your Website against Niche Leaders to Determine Content Helpfulness and Reliability
Your market research will help you select “good” sites with your business nice. Combine a manual review of them along with using tools for data insights; together they provide guidance as you benchmark your progress.
Conduct deep dives into how competitive websites drive traffic, promote growth, and connect with users. If you have traffic loss to your website, this helps to capitalize quickly on opportunities as well as mitigate risks fast.
Google’s Danny Sullivan has stressed the importance of assessing the helpfulness, usefulness, and reliability of individual content and your sites as a whole. He acknowledged that Google’s systems are imperfect and a high-quality site may miss sufficient.
“Some of them ranking really well. But they’ve moved down a bit in small positions enough that the traffic drop is notable. They assume they have fundamental issues but don’t, really — which is why we added a whole section about this to our debugging traffic drops page.” – Danny Sullivan on X [7]
Google will be seeking whether you add “original information, reporting, research, or analysis.” ChatGPT and generative AI-based SEO Tools JUST scrape the top search results. That is not necessarily going to create anything new. Instead, it will just rehash what search engines already show users.
One way to pull out of a traffic drop is to add information gain to those lagging pages. This means adding deeper insights and value for your audience. Google emphasises this, when it asks “Does the content provide substantial value when compared to other pages in search results?”
Updates to Google’s Debugging Traffic Drops Documentation
April 26, 2024, Google updated its debugging traffic drops documentation. The most significant changes are highlighted below:
- Algorithmic updates: Its documentation expands on the impact of algorithmic updates and how to identify them.
- Policy and manual actions: The section on policy and manual actions organic traffic drops have a significant change. The part that stated, “most traffic drops can be reversed,” is gone. Now, it emphasizes that understanding what happened is not straightforward.
- Example charts: The visual charts used to describe reasons for organic traffic drops have been updated.
Websites can lose significant organic traffic from Google’s Core updates and find it challenging to analyze rank changes. Often, a hidden cause is ultra-fine intent shifts. Outdated models and auditing practices commonly fail to reveal what’s really occurring.
It helps to think beyond user intent as transactional, navigational, informational, and commercial. We see that search results’ placements and values are different by assessing traffic drops with refined and specific data that has strong varsity.
Google categorizes its top results into:
- Dominant intent.
- Common intent.
- Minor intent.
Google SERPS often display a mix of results when attempting to answer each of those intents; its search filters, People Also Ask and People Also Search For features help searchers get more ideal answers.
Below are insights I like from other experts.
“Google recently published 3 updates that had a big impact on organic traffic across many verticals. If you were recieving a lot of traffic from HowTo web pages, the fact that the search engine has now dropped HowTo rich results may impact your traffic levels.
…one recognizable pattern is what I call domain flips. Google core updates tend to reward domains for good quality, which can come down to fine differences. When the keyword overlap between domains is high, and they go head to head with each other, they can fight for the same real estate on Google.” – Google’s latest updates leave no room for low-quality content by Kevin Indig [6]
“How long does it take to recover after a Google core update hit?
If you are able to improve your content quality and E-E-A-T, you may see some incremental improvements in the months that follow, but in most cases where we have seen good recoveries, we have needed to wait until the next Google core update. In some cases, it can take two core updates in order to see your quality improvements rewarded. Again, core updates happen a few times per year. – Google’s Helpful Content Update by Marie Haynes
SUMMARY: Stay on Top of Factors that may Cause Traffic Declines
In most cases it is possible to recover your lost web traffic. Your drop in Google traffic may also be caused by position drops, external market factors, or other emerging SERP opportunities you’re missing and your competition has taken advantage of. Fewer user searches, a sharp product interest decline, a Google Ads strategy change, tagging issues (such as moving to GA4 from Universal Analytics), etc.
Contact us today to Comprehensively Audit Your Website
References
[1] https://twitter.com/lilyraynyc/status/1643732854181089280?s=20
[2] https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/robots/intro
[3] https://twitter.com/JohnMu/status/1643994172830154753?s=20
[4] https://twitter.com/flytyingguy/status/1643379522006556672
[5] https://developers.google.com/search/docs/essentials
[6] https://www.kevin-indig.com/googles-latest-updates/
[7] https://developers.google.com/search/docs/monitor-debug/debugging-search-traffic-drops